Toolkit Home | Toolkit | Case Studies | Change Leader Moves Resources by Category | Suggested Readings
RESOURCE LIBRARY
The resources curated in this online library are aimed to help leaders who are engaging in a systemic change project.
Systemic change is a change that affects multiple courses, departments, programs, divisions, colleges (or beyond) and results in changes that affect policies, procedures, norms, cultures, and/or structures (organizational, curricular, fiscal). This resource library offers existing tools and readings you can access to support change efforts at your institution. The categorization is broken down by tools that cover leadership style resources, systemic change-based resources, overcoming barriers resources, and then by Change Leader Moves resources.
This resource library complements our comprehensive Change Leadership Toolkit (CLT) and our Case Studies (available Spring 2023).
Systemic Change Based Resources:
- Keck/PKAL Model for Systemic Institutional Change in STEM Education
- Framework For Systemic Change In Undergraduate Stem Teaching And Learning
Change Leader Moves Resources by Category
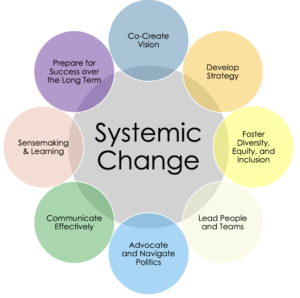
CHANGE LEADER MOVES RESOURCES BY CATEGORY

Create Vision, Expectations and Pacing: These moves result in the development and articulation of a shared vision drawing widely from campus stakeholders as well as articulation of goals, outcomes, and timing. This vision is most successful when aligned with the institution’s mission and must be cognizant of prior relevant systemic change efforts (successful or otherwise).
Resources
- Creating Shared Vision: A Tip Sheet from REvolutionizing engineering and computer science Departments (RED) Participatory Action Research
- Design for Equity in Higher Education
- Changemakers: The Student Success North Star
- Changemakers: Transformation Timeline

Develop Strategy and Resources: These moves result in the development of an appropriate set of plans that include actions that are equitable to reach the desired vision as well as organization of revenue (with an eye/lens on who is impacted), infrastructure, and people resources needed to be successful.
Resources
- Creating Strategic Partnerships: A Tip Sheet from Revolutionizing Engineering Departments (RED) Participatory Action Research
- Leading Highly Effective External Strategic Partnerships
- Tools in a Toolbox: Leading Change in Community Colleges
- Strategies for Successful Change
- Barriers to Innovation and Change in Higher Education
- Changemakers: Planning Next Steps
- Changemakers: Assessing and Prioritizing Initiatives

Foster Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion: These moves ensure attention to diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) throughout the initiative. They involve using a DEI lens to situate the work, develop strategies, address cultural issues, and ensure the inclusion of diverse voices and perspectives across social identities (e.g., Women, BIPOC, 1stGen, etc.), positional identities (e.g., student, faculty, staff) and other constituents’ interests (e.g. community members).
Resources
- Shared Equity Leadership Making Equity Everyone’s Work
- Organizing Shared Equity Leadership: Four Approaches to Structuring the Work
- Shared Equity Leadership Toolkit
- Shared Responsibility Means Shared Accountability: Rethinking Accountability Within Shared Equity Leadership
- Center for Urban Education Observation Tool

Lead People and Teams: These moves result in the development of high-functioning individuals and teams that drive success in any systemic change initiative. Leadership teams should be diverse not just in terms of disciplinary background or expertise but also social identities and life experience. They should be organized with expertise and perspectives focused on the change goals, inclusive of appropriate stakeholders, and attentive to the development and empowerment of leaders.
Resources
- Campus and Community Conversations Working Together for Community College Student Success
- Student Success Teams: An Implementation Guide for Community Colleges
- Forming And Developing Teams: A Tip Sheet from REvolutionizing Engineering Departments (RED) Participatory Action Research
- Readiness Survey
- Shared Leadership in Higher Education
- Immunity to Change Worksheets
- Guide For Composing a Campus Racial Equity Team
- Center for Urban Education Embedding Equity Mindedness Tool
- Bolman and Deal Leadership Orientations Self-Assessment
- Changemakers: Building a Team
- Changemakers: Bringing a Student Voice into the Room
 Engage in Advocacy and Navigate Politics: These moves relate to understanding the dynamics of power and influence (informal and formal) and how to navigate them to achieve change goals, from recruiting key influencers to changing the minds of skeptics to making the case to those in decision-making positions. These moves also include effectively advocating for the change to various audiences in order to gain support and foster success.
Engage in Advocacy and Navigate Politics: These moves relate to understanding the dynamics of power and influence (informal and formal) and how to navigate them to achieve change goals, from recruiting key influencers to changing the minds of skeptics to making the case to those in decision-making positions. These moves also include effectively advocating for the change to various audiences in order to gain support and foster success.
Resources
- Buy In Worksheet
- Scaling change in higher education: A guide for stakeholder groups
- Understanding Leadership Strategies for Addressing the Politics of Diversity
- Navigating Politics: A Requirement for Career Success
- Political Savvy & Leadership Effectiveness
- Change Buy in Worksheet to Changemakers: Gaining Buy-In
 Communicate Effectively: These moves result in strong communication about the change initiative, both internally and externally. Effective communication includes crafting messages that inclusively engage stakeholders in conversations, telling meaningful stories, and soliciting and listening to feedback to amplify the voices of change makers as well as success.
Communicate Effectively: These moves result in strong communication about the change initiative, both internally and externally. Effective communication includes crafting messages that inclusively engage stakeholders in conversations, telling meaningful stories, and soliciting and listening to feedback to amplify the voices of change makers as well as success.
Resources
- Communicating Change: A Tip Sheet from Revolutionizing Engineering Departments (RED) Participatory Action Research
- Are We There Yet? A Communications Evaluation Guide
- Achieving the Dream: Communication Strategy Guidelines for Network Colleges
- Achieving the Dream: Communication Strategy and Work Plan Templates
- Changemakers: Team Brainstorm
 Sensemake and Learn: These moves involve using data and information to understand perceptions, raise consciousness, and to bridge gaps in current and needed knowledge and understanding in order to ensure strong organizational learning and development.
Sensemake and Learn: These moves involve using data and information to understand perceptions, raise consciousness, and to bridge gaps in current and needed knowledge and understanding in order to ensure strong organizational learning and development.
Resources
- SENSEMAKING: Framing and Acting in the Unknown
- Using a Systems Approach to Change: Examining the AAU Undergraduate STEM Education Initiative
- The Framework for Systemic Change in Undergraduate STEM Teaching and Learning
- Keck/PKAL Model for Systemic Institutional Change in STEM Education: Stage Five: Determine Readiness for Action (p.69)
- Readiness Survey
- Changemakers: Initiative Inspiration
- Changemakers: Initiative Blueprint
 Prepare for Success Over the Long Term: These moves result in long-term project success and include ensuring ways to measure success and maintain momentum, identifying appropriate infrastructure required to scale and sustain the change (e.g., budget, policy, process, physical plant), building motivation and emotional support, understanding the human toll of change, and identifying next steps beyond the current project.
Prepare for Success Over the Long Term: These moves result in long-term project success and include ensuring ways to measure success and maintain momentum, identifying appropriate infrastructure required to scale and sustain the change (e.g., budget, policy, process, physical plant), building motivation and emotional support, understanding the human toll of change, and identifying next steps beyond the current project.
Resources
Suggested Readings
Fry, C.L. PhD. (ed). (2014) Achieving Systemic Change: A Sourcebook for Advancing and Funding Undergraduate STEM Education. Washington, D.C.: The Association of American Colleges and Universities. Retrieved from https://www.aau.edu/sites/default/files/AAU-Files/STEM-Education-Initiative/E-PKALSourcebook.pdf
Kezar, A. (2018). How colleges change: Understanding, leading, and enacting change. Routledge.
Kezar, A., & Miller E.R. (2020). Using a Systems Approach to Change: Examining the AAU Undergraduate STEM Education Initiative. In White, K., Beach, A., Finkelstein, N., Henderson, C., Simkins, S., Slakey, L., Stains, M., Weaver, G., & Whitehead, L. (Eds. Pressbooks. http://openbooks.library.umass.edu/ascnti2020/
Meadows, D. (1999). Leverage points. Places to Intervene in a System, 19.